If you need an FHA loan to buy a home or refinance, then you have until April 6th to call me, before the cost goes up. Plus, we have new updates on the HARP 2.0 government refi program, and it’s good news! Watch today’s video for details.
Tag: homeowners
-
Collecting GFE’s Isn’t the Best Way to Compare Mortgages
On a daily basis, I get calls from people who just want a Good Faith Estimate, as they are shopping for a mortgage loan. In today’s video, I explain why this isn’t the best practice and what you should do to get the best deal!
-
Have Dinner on Us for Next 30 Years!
How much do you spend when you go out to dinner with your family or friends? What if I could show you how I can cover that cost for the next 30 years? Watch today’s video for details!
-
What you should know about Mortgage Debt Forgiveness
Starting today, I will not be publishing rates online anymore. In this video, I explain why and how you can get an accurate refinance or purchase loan. Plus, some fact about Mortgage-Debt-Forgiveness that you should know! Get an accurate rate quote for your loan at www.GoNorthwestLoans.com
-
Why Younger Generation Should Buy a Home Right Now!
So many young people either don’t think they can afford a home, or hold off due to fear of the markets. However, right now is an amazing time to buy! In today’s video, I explain what a very small down-payment can mean in 5 or 10 years down the line – incredible!
-
Today’s solar flare may affect housing – really?
Today, the Earth is facing a direct blow from the Sun … and I’m not talking about warm temps. Plus, Congress is looking to raise home loan fees yet again … watch video for details!
-
Buyer’s market forming – and why your mortgage rate doesn’t matter!
Big housing market shift has created more competition for those that want to buy homes. Watch for details, and I will also explain why the lowest interest rate isn’t always the best deal for you!
-
Buy your next home WITHOUT selling your current one first!
Many people believe the only way they can buy a new home, is by selling their existing one first. Not necessarily true, and your dream home might just be a phone call away!
-
Should you take the lowest rate, or lower closing costs?
Let’s clear up some common confusion … are you better off with the lowest interest rate, or should you take a slightly higher rate with much lower closing costs? I explain in today’s video.
-
CoreLogic: 11.1 Million U.S. Properties with Negative Equity in Q4, Calculatedriskblog.com
CoreLogic released the Q4 2011 negative equity report today.
CoreLogic … today released negative equity data showing that 11.1 million, or 22.8 percent, of all residential properties with a mortgage were in negative equity at the end of the fourth quarter of 2011. This is up from 10.7 million properties, 22.1 percent, in the third quarter of 2011. An additional 2.5 million borrowers had less than five percent equity, referred to as near-negative equity, in the fourth quarter. Together, negative equity and near-negative equity mortgages accounted for 27.8 percent of all residential properties with a mortgage nationwide in the fourth quarter, up from 27.1 in the previous quarter. Nationally, the total mortgage debt outstanding on properties in negative equity increased from $2.7 trillion in the third quarter to $2.8 trillion in the fourth quarter.
“Due to the seasonal declines in home prices and slowing foreclosure pipeline which is depressing home prices, the negative equity share rose in late 2011. The negative equity share is back to the same level as Q3 2009, which is when we began reporting negative equity using this methodology. The high level of negative equity and the inability to pay is the ‘double trigger’ of default, and the reason we have such a significant foreclosure pipeline. While the economic recovery will reduce the propensity of the inability to pay trigger, negative equity will take an extended period of time to improve, and if there is a hiccup in the economic recovery, it could mean a rise in foreclosures.” said Mark Fleming, chief economist with CoreLogic.
Here are a couple of graphs from the report:
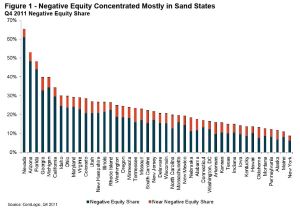 Click on graph for larger image.
Click on graph for larger image.This graph shows the break down of negative equity by state. Note: Data not available for some states. From CoreLogic:
“Nevada had the highest negative equity percentage with 61 percent of all of its mortgaged properties underwater, followed by Arizona (48 percent), Florida (44 percent), Michigan (35 percent) and Georgia (33 percent). This is the second consecutive quarter that Georgia was in the top five, surpassing California (29 percent) which previously had been in the top five since tracking began in 2009. The top five states combined have an average negative equity share of 44.3 percent, while the remaining states have a combined average negative equity share of 15.3 percent.”
 The second graph shows the distribution of equity by state- black is Loan-to-value (LTV) of less than 80%, blue is 80% to 100%, red is a LTV of greater than 100% (or negative equity). Note: This only includes homeowners with a mortgage – about 31% of homeowners nationwide do not have a mortgage.
The second graph shows the distribution of equity by state- black is Loan-to-value (LTV) of less than 80%, blue is 80% to 100%, red is a LTV of greater than 100% (or negative equity). Note: This only includes homeowners with a mortgage – about 31% of homeowners nationwide do not have a mortgage.Some states – like New York – have a large percentage of borrowers with more than 20% equity, and Nevada, Arizona and Florida have the fewest borrowers with more than 20% equity.
Some interesting data on borrowers with and without home equity loans from CoreLogic: “Of the 11.1 million upside-down borrowers, there are 6.7 million first liens without home equity loans. This group of borrowers has an average mortgage balance of $219,000 and is underwater by an average of $51,000 or an LTV ratio of 130 percent.
The remaining 4.4 million upside-down borrowers had both first and second liens. Their average mortgage balance was $306,000 and they were upside down by an average of $84,000 or a combined LTV of 138 percent.”
Related articles
- 22.8 Percent of U.S. Homes Are Underwater (bingrealtygroup.wordpress.com)
- Number of Under Water Borrowers Rises (blogs.wsj.com)
- Housing Still Drowning in Underwater Mortgages (blogs.wsj.com)
- Two Thirds Of All Nevada Mortgages Are Underwater (zerohedge.com)
- Property market: How 2011 is shaping up (confused.com)
- There is ‘no silver bullet’ to address mortgage arrears, says financial regulator (teddyoshea.wordpress.com)
- Help for those trapped in negative equity (gateway-homes.co.uk)
- Mortgage delinquencies up in November, down for the year (agbeat.com)
- More Oregon, Portland-area mortgages underwater at year’s end (oregonlive.com)
- Why Those Pre Approval Letters Are So Important (nangoebel.wordpress.com)
-
What are “normal” closing costs for home loans?
Many people ask me how much closing costs are, to figure out what the best deal is for their home loan. In today’s video I detail what’s normal and how to avoid paying too much!
-
Mortgage market over-correction, or a sign of things to come?
In the past two days, mortgage rates have risen across the board by an average of 1/4%. This is significant and affects buying power & payments. Will this continue? Watch today as I give my predictions!
-
America’s Credit and Housing Crisis: New State Bank Bills, Marketoracle.co.uk
Seventeen states have now introduced bills for state-owned banks, and others are in the works. Hawaii’s innovative state bank bill addresses the foreclosure mess. County-owned banks are being proposed that would tackle the housing crisis by exercising the right of eminent domain on abandoned and foreclosed properties. Arizona has a bill that would do this for homeowners who are current in their payments but underwater, allowing them to refinance at fair market value.
The long-awaited settlement between 49 state Attorneys General and the big five robo-signing banks is proving to be a majordisappointment before it has even been signed, sealed and court approved. Critics maintain that the bankers responsible for the housing crisis and the jobs crisis will again be buying their way out of jail, and the curtain will again drop on the scene of the crime.
We may not be able to beat the banks, but we don’t have to play their game. We can take our marbles and go home. The Move Your Money campaign has already prompted more than 600,000 consumers to move their funds out of Wall Street banks into local banks, and there are much larger pools that could be pulled out in the form of state revenues. States generally deposit their revenues and invest their capital with large Wall Street banks, which use those hefty sums to speculate, invest abroad, and buy up the local banks that service our communities and local economies. The states receive a modest interest, and Wall Street lends the money back at much higher interest.
Rhode Island is a case in point. In an article titled “Where Are R.I. Revenues Being Invested? Not Locally,” Kyle Hence wrote in ecoRI Newson January 26th:
According to a December Treasury report, only 10 percent of Rhode Island’s short-term investments reside in truly local in-state banks, namely Washington Trust and BankRI. Meanwhile, 40 percent of these investments were placed with foreign-owned banks, including a British-government owned bank under investigation by the European Union.
Further, millions have been invested by Rhode Island in a fund created by a global buyout firm . . . . From 2008 to mid-2010, the fund lost 10 percent of its value — more than $2 million. . . . Three of four of Rhode Island’s representatives in Washington, D.C., count [this fund] amongst their top 25 political campaign donors . . . .
Hence asks:
Are Rhode Islanders and the state economy being served well here? Is it not time for the state to more fully invest directly in Rhode Island, either through local banks more deeply rooted in the community or through the creation of a new state-owned bank?
Hence observes that state-owned banks are “[o]ne emerging solution being widely considered nationwide . . . . Since the onset of the economic collapse about five years ago, 16 states have studied or explored creating state-owned banks, according to a recent Associated Press report.”
2012 Additions to the Public Bank Movement
Make that 17 states, including three joining the list of states introducing state bank bills in 2012: Idaho (a bill for a feasibility study), New Hampshire (a bill for a bank), and Vermont (introducing THREE bills—one for a state bank study, one for a state currency, and one for a state voucher/warrant system). With North Dakota, which has had its own bank for nearly a century, that makes 18 states that have introduced bills in one form or another—36% of U.S. states. For states and text of bills, see here.
Other recent state bank developments were in Virginia, Hawaii, Washington State, and California, all of which have upgraded from bills to study the feasibility of a state-owned bank to bills to actually establish a bank. The most recent, California’s new bill, was introduced on Friday, February 24th.
All of these bills point to the Bank of North Dakota as their model. Kyle Hence notes that North Dakota has maintained a thriving economy throughout the current recession:
One of the reasons, some say, is the Bank of North Dakota, which was formed in 1919 and is the only state-owned or public bank in the United States. All state revenues flow into the Bank of North Dakota and back out into the state in the form of loans.
Since 2008, while servicing student, agricultural and energy— including wind — sector loans within North Dakota, every dollar of profit by the bank, which has added up to tens of millions, flows back into state coffers and directly supports the needs of the state in ways private banks do not.
Publicly-owned Banks and the Housing Crisis
A novel approach is taken in the new Hawaii bill: it proposes a program to deal with the housing crisis and the widespread problem of breaks in the chain of title due to robo-signing, faulty assignments, and MERS. (For more on this problem, see here.) According to a February 10th report on the bill from the Hawaii House Committees on Economic Revitalization and Business & Housing:
The purpose of this measure is to establish the bank of the State of Hawaii in order to develop a program to acquire residential property in situations where the mortgagor is an owner-occupant who has defaulted on a mortgage or been denied a mortgage loan modification and the mortgagee is a securitized trust that cannot adequately demonstrate that it is a holder in due course.
The bill provides that in cases of foreclosure in which the mortgagee cannot prove its right to foreclose or to collect on the mortgage, foreclosure shall be stayed and the bank of the State of Hawaii may offer to buy the property from the owner-occupant for a sum not exceeding 75% of the principal balance due on the mortgage loan. The bank of the State of Hawaii can then rent or sell the property back to the owner-occupant at a fair price on reasonable terms.
Arizona Senate Bill 1451, which just passed the Senate Banking Committee 6 to 0, would do something similar for homeowners who are current on their payments but whose mortgages are underwater (exceeding the property’s current fair market value). Martin Andelman callsthe bill a “revolutionary approach to revitalizing the state’s increasingly water-logged housing market, which has left over 500,000 ofArizona’s homeowners in a hopelessly immobile state.”
The bill would establish an Arizona Housing Finance Reform Authority to refinance the mortgages of Arizona homeowners who owe more than their homes are currently worth. The existing mortgage would be replaced with a new mortgage from AHFRA in an amount up to 125% of the home’s current fair market value. The existing lender would get paid 101% of the home’s fair market value, and would get a non-interest-bearing note called a “loss recapture certificate” covering a portion of any underwater amounts, to be paid over time. The capital to refinance the mortgages would come from floating revenue bonds, and payment on the bonds would come solely from monies paid by the homeowner-borrowers. An Arizona Home Insurance Fund would create a cash reserve of up to 20 percent of the bond and would be used to insure against losses. The bill would thus cost the state nothing.
Critics of the Arizona bill maintain that it shifts losses from collapsed property values onto banks and investors, violating the law of contracts; and critics of the Hawaii bill maintain that the state bank could wind up having paid more than market value for a slew of underwater homes. An option that would avoid both of these objections is one suggested by Michael Sauvante of the Commonwealth Group, discussed earlierhere: the state or county could exercise its right of eminent domain on blighted, foreclosed and abandoned properties. It could offer to pay fair market value to anyone who could prove title (something that with today’s defective title records normally can’t be done), then dispose of the property through a publicly-owned land bank as equity and fairness dictates. If a bank or trust could prove title, the claimant would get fair market value, which would be no less than it would have gotten at an auction; and if it could not prove title, it legally would have no claim to the property. Investors who could prove actual monetary damages would still have an unsecured claim in equity against the mortgagors for any sums owed.
Rhode Island Next?
As the housing crisis lingers on with little sign of relief from the Feds, innovative state and local solutions like these are gaining adherents in other states; and one of them is Rhode Island, which is in serious need of relief. According to The Pew Center on the States, “The country’s smallest state . . . was one of the first states to fall into the recession because of the housing crisis and may be one of the last to emerge.”
Rhode Islanders are proud of having been first in a number of more positive achievements, including being the first of the 13 original colonies to declare independence from British rule. A state bank presentation was made to the president of the Rhode Island Senate and other key leaders earlier this month that was reportedly well received. Proponents have ambitions of making Rhode Island the first state in this century to move its money out of Wall Street into its own state bank, one owned and operated by the people for the people.
Ellen Brown is an attorney and president of the Public Banking Institute, http://PublicBankingInstitute.org. In Web of Debt, her latest of eleven books, she shows how a private cartel has usurped the power to create money from the people themselves, and how we the people can get it back. Her websites are http://WebofDebt.com and http://EllenBrown.com.
Ellen Brown is a frequent contributor to Global Research. Global Research Articles by Ellen Brown
© Copyright Ellen Brown 2012
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are the sole responsibility of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of the Centre for Research on Globalization. The contents of this article are of sole responsibility of the author(s). The Centre for Research on Globalization will not be responsible or liable for any inaccurate or incorrect statements contained in this article.
http://www.marketoracle.co.uk/Article33365.html
Related articles
- Move Our Money: Should we create more state banks? (energybulletin.net)
- New State Bank Bills Address Credit and Housing Crises (webofdebt.wordpress.com)
- North Dakota bank eyed by cash-hungry politicians (sfgate.com)
- Rhode Island drops Fordham 78-58 (newsok.com)
- Structural Reform: The Case for Public State Banks (beavercountyblue.org)
- Rhode Island En Route To Upgrading Crappy Civil Unions To Real Gay Marriages (queerty.com)
- Forget Texas, check out North Dakota (skydancingblog.com)
- Economic struggles spur calls for public banking (usatoday.com)
- A legislative solution for RI’s compassion centers? (wrnihealthcareblog.wordpress.com)
-
MERS
What we need to do is take a survey, the population being made up of mortgage borrowers between the years 2002-2008. Why these years would become apparent with the results, which can be predicted before ever tallying the results. It would be a one question survey:
“Upon loan origination, was it required, in addition to completing a loan 1003 loan application, that you also provide specific documents for verification and loan qualification purposes, or did you simply have to complete a loan 1003 loan application?”
My bet would be that most everyone who was in receipt of a loan prior to September 2005 was required to submit documents to a human person which were used to verify loan qualification. Most nearly everyone subsequent that date was not required to submit anything by way of supporting documents.
This gives us two separately defined groups:
GROUP A: borrowers whose loans were humanly underwritten and verified
GROUP B: borrowers whose loans were underwritten entirely by automation
We can argue about the underlying reasons for economic collapse all day long, as there are certainly many, but one fact remains as being integral. This is acknowledging that there were borrowers that never, ever should have been approved for a loan, yet were. It was this very small subset of borrowers in Group B however, those that defaulted nearly immediately, that is within the first through third months out of the gate. It was these ‘early payment defaults (EPD’s ) that spread throughout the investment community causing fear, bringing into question the quality of all loan originations, thereby freezing the credit markets in August 2007, a year later the entire economy collapsed.
Of course, it is much more complex than that, but the crucial piece that provided the catalyst was these EPD’s. It was the quality of the borrowers from these EPD’s that became the model by which was used to stigmatize all borrowers. What was needed was a fall guy, to first lessen the anger towards the bailouts in providing a scapegoat, and second to divert attention away from the facts underlying the lending standards the failed and/or intentionally purposeful failure of the automation. From my research, it was with purposeful intent come hell or high water is my mission in life to bring forth into the public light.
Putting intent aside for the moment and just focusing on the EPD’s and the domino effect they caused which resulted in millions of borrowers, from both Groups A and B, to lose their homes or struggling to hold on. How could one small group of failed borrowers affect millions of other borrowers, especially those who were qualified through the traditional methods of underwriting?
The answer is an obvious one, coming down to the one common element that is the structuring of the loan products, that as it relates to the reset. Anyone whose reset occurred just prior and certainly after the economic collapse was as the saying goes…..Screwed. It is within is this, that the Grand Illusion lay intentionally concealed and hidden. It is within the automation wherein all the evidence clearly points to the fact that a mortgage is not a mortgage but rather a basket of securities….Not just any securities, but debt defaultable securities. In other words, it was largely planned to intentionally give loans to those whom were known to result in default.
But, even without understanding any of the issues as to the ‘basket of securities” there is one obvious point that looms, hiding in plain sight, which I believe should be completely exploited. This as it directly relates to our mortal enemy, that which takes the name of MERS. I know there are those that disseminate the structure of Mortgage Electronic Registration Systems, Inc and Merscorp as it relates to the MIN number and want to pick it apart, and all this is well and good. However, they miss the larger and more obvious point that clearly gives some definition.
There is one particular that every one of those millions upon millions of borrowers, those in both Group A and Group B along with the small subset of Group B, all have in common. ……MERS. MERS was integrated into every set of loan documents, slide past the borrowers without explanation without proper representation in concealing the implied contracts behind the trade and service mark of MERS.
MERS does not discriminate between a good or a bad loan, a loan is a loan as far it is concerned, whether it was fraudulently underwritten or perfectly underwritten. If it is registered with MERS the good, the bad, the ugly all go down, and therein lays an issue that is pertinent to discussion.
MERS was written into all Fannie and Freddie Uniform Security Instrument, not by happenstance, rather mandated by Fannie and Freddie. It was they who crafted verbiage and placement within the document. Fannie and Freddie are of course agency loans, however nearly 100% of non-agency lenders utilized the same Fannie and Freddie forms. Put into context, MERS covers both agency and non-agency, and not surprisingly members of MERS as well. Talk about fixing the game!!
It would seem logical, considering we, the American Taxpayer own Fannie Mae, that we should be entitled some answers to some very basic questions……The primary question: If Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac mandated that MERS play the role that it does, why than were there no quality control measures in place, and should they not have been responsible for putting in some safety measures in place?
The question is a logical one; any other business would have buried in litigation had a product it sponsored or mandated, as the case may be here, resulted in complete failure. From the standpoint of public policy, MERS was a tremendous failure. Why? The answer derives itself from the facts as laid out above regarding the underwriting processes and the division of borrowers: Group A and B.
This becomes a pertinent taking into account Fannie Mae on record in its recorded patents.
US PATENT #7,881,994 B1– Filed April 1, 2004, Assignee: Fannie Mae
‘It is well known that low doc loans bear additional risk. It is also true that these loans are
charged higher rates in order to compensate for the increased risk.’
System and method for processing a loan
US PATENT # 7,653,592– Filed December 30, 2005, Assignee: Fannie Mae
The following from the Summary section states:
‘An exemplary embodiment relates to a computer-implemented mortgage loan application data processing system comprising user interface logic and a workflow engine. The user interface logic is accessible by a borrower and is configured to receive mortgage loan application data for a mortgage loan application from the borrower. The workflow engine has stored therein a list representing tasks that need to be performed in connection with a mortgage loan application for a mortgage loan for the borrower. The tasks include tasks for fulfillment of underwriting conditions generated by an automated underwriting engine. The workflow engine is configured to cooperate with the user interface logic to prompt the borrower to perform the tasks represented in the list including the tasks for the fulfillment of the underwriting conditions. The system is configured to provide the borrower with a fully-verified approval for the mortgage loan application. The fully-verified approval indicates that the mortgage loan application data received from the borrower has already been verified as accurate using information from trusted sources. The fully-verified approval is provided in a form that allows the mortgage loan application to be provided to different lenders with the different lenders being able to authenticate the fully-verified approval status of the mortgage loan application’
Computerized systems and methods for facilitating the flow of capital
through the housing finance industry
US PATENT # 7,765,151– Filed July 21, 2006, Assignee: Fannie Mae
The following passages taken from patent documents reads:
‘The prospect or other loan originator preferably displays generic interest rates (together with an assumptive rate sheet, i.e., current mortgage rates) on its Internet web site or the like to entice online mortgage shoppers to access the web site (step 50). The generic interest rates (“enticement rates”) displayed are not intended to be borrower specific, but are calculated by pricing engine 22 and provided to the loan originator as representative, for example, of interest rates that a “typical” borrower may expect to receive, or rates that a fictitious highly qualified borrower may expect to receive, as described in greater detail hereinafter. FIG. 2b depicts an example of a computer Internet interface screen displaying enticement rates.’
’If the potential borrower enters a combination of factors that is ineligible, the borrower is notified immediately of the ineligibility and is prompted to either change the selection or call a help center for assistance (action 116). It should be understood that this allows the potential borrower to change the response to a previous question and then continue on with the probable qualification process. If the potential borrower passes the eligibility screening, the borrower then is permitted to continue on with the probable qualification assessment.’
‘Underwriting engine 24 also determines, for each approved product, the minimum amount of verification documentation (e.g., minimum assets to verify, minimum income to verify), selected loan underwriting parameters, assuming no other data changes, (e.g., maximum loan amount for approval, maximum loan amount for aggregating closing costs with the loan principal, and minimum refinance amount), as well as the maximums and minimums used to tailor the interest rate quote (maximum schedule interest rate and maximum number of points) and maximum interest rate approved for float up to a preselected increase over a current approved rate. It should be appreciated that this allows the potential borrower to provide only that information that is necessary for an approval decision, rather than all potentially relevant financial and other borrower information. This also reduces the processing burden on system.’
The two patents above was Fannie Mae’s means of responding to its competition, that being the non-agency who had surpassed the agencies in sales volume (those stats I will have to dig up and repost as they are not handy at the moment), as the non-agencies had dropped all standards back in and around September 2005.
The point being though, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mad were the caretakers of MERS, so to speak, inasmuch as mandating MERS upon the borrowers. Had there been safety measures in place that caught the fact that the loans that were dumping out quickly, that is the EPD’s, there might have been a stoppage in place, thereby preventing MERS from executing foreclosures upon every successive mortgage.
I know that this is all BS though, because it is a cover up, a massive one that cuts into the heart of the United States government. This is perhaps one avenue by which to get there, as the questions asked are easily understood, as opposed to digging into the automation processes which people apparently are not ready to accept as of yet.
-
Fannie, Freddie overhaul unlikely, by Vicki Needham, Thehill.com
An overhaul of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac is unlikely again this year despite recent Republican efforts to move the issue up the agenda.
Congressional Republicans, along with some Democrats — and even GOP presidential candidate Newt Gingrich — are renewing calls to craft an agreement to reduce the involvement of Fannie and Freddie in the nation’s mortgage market.
But without a broader accord, passage of any legislation this year is slim, housing experts say.
Jim Tobin, senior vice president of government affairs for the National Association of Home Builders, concedes that despite a mix of Democratic and Republican proposals, including a push by the Obama administration last year, congressional leaders probably won’t get far this year on a plan for Fannie and Freddie, the government-controlled mortgage giants.
Tobin said there are “good ideas out there” and while he expects the House to put some bills on the floor and possibly pass legislation, the Senate is likely to remain in oversight mode without any “broad-based legislation on housing finance.”
“We’re bracing for a year where it’s difficult to break through on important policy issues,” he said this week.
While the issue makes for a good talking point, especially in an presidential election year, congressional efforts are largely being stymied by the housing market’s sluggish recovery, prohibiting the hand off between the government and private sector in mortgage financing, housing experts say.
David Crowe, chief economist with NAHB, said that the market has hit rock bottom and is now undergoing a “slow climb out of the hole.”
The House has taken the biggest steps so far — by mid-July the Financial Services Committee had approved 14 bills intended to jump-start reform of the government-sponsored enterprises.
“As we continue to move immediate reforms, our ultimate goal remains, to end the bailout of Fannie, Freddie and build a stronger housing finance system that no longer relies on government guarantees,” panel Chairman Spencer Bachus (R-Ala.) said last summer.
Meanwhile, a number of GOP and bipartisan measures have emerged — Democrats and Republicans generally agree Fannie and Freddie are in need of a fix but their ideas still widely vary.
There are a handful of bills floating around Congress, including one by Reps. John Campbell (R-Calif.) and Gary Peters (D-Mich.), and another by Reps. Gary Miller (R-Calif.) and Carolyn Maloney (D-N.Y), which would wind down Fannie and Freddie and create a new system of privately financed organizations to support the mortgage market.
“Every one of those approaches replaces them [Fannie and Freddie] with what they think is the best alternative to having a new system going forward that would really fix the problem and would really give certainty to the marketplace and allow housing finance to come back, and therefore housing to come back, as well,” Campbell said at a markup last month.
There’s another bill by Rep. Jeb Hensarling (R-Texas) and bills in the Senate being pushed by Sens. Bob Corker (R-Tenn.) and Johnny Isakson (R-Ga.).
Corker, a member of the Senate Banking Committee, made the case earlier this week for unwinding government support for the GSEs while promoting his 10-year plan that would put in place the “infrastructure for the private sector to step in behind it.”
“A big part of the problem right now is the private sector is on strike,” Corker said.
He has argued that his bill isn’t a silver bullet, rather a conversation starter to accelerate talks.
“So what we need to do is figure out an orderly wind-down,” Corker said in November. “And so we’ve been working on this for some time. We know that Fannie and Freddie cannot exist in the future.”
He suggested getting the federal government this year to gradually wind down the amount of the loans it guarantees from 90 percent to 80 percent and then to 70 percent.
“And as that drops down, we think the market will send signals as to what the difference in price is between what the government is actually guaranteeing and what they’re not,” he said.
Even Gingrich, who has taken heat for his involvement with taking money while doing consulting work for the GSEs, called for an unwinding during a December interview.
“I do, in fact, favor breaking both of them up,” he said on CBS’ Face the Nation. “I’ve said each of them should devolve into probably four or five companies. And they should be weaned off of the government endorsements, because it has given them both inappropriate advantages and because we now know from the history of how they evolved, that they abused that kind of responsibility.”
In a white paper on housing last week, the Federal Reserve argued that the mortgage giants should take a more active role in boosting the housing market, although they didn’t outline suggestions for how to fix the agencies.
The central bank did argue that “some actions that cause greater losses to be sustained by the GSEs in the near term might be in the interest of taxpayers to pursue if those actions result in a quicker and more vigorous economic recovery.”
Nearly a year ago, Treasury Secretary Timothy Geithner asked Congress to approve legislation overhauling Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac within two years — that deadline appears to be in jeopardy.
The Obama administration’s initial recommendations called for inviting private dollars to crowd out government support for home loans. The white paper released in February proposed three options for the nation’s housing market after Fannie and Freddie are wound down, with varying roles for the government to play.
About the same time last year, Bachus made ending the “taxpayer-funded bailout of Fannie and Freddie” the panel’s first priority.
While an overhaul remains stalled for now there is plenty of other activity on several fronts.
In November, the Financial Services panel overwhelmingly approved a measure to stop future bonuses and suspend the current multi-million dollar compensation packages for the top executives at the agencies.
The top executives came under fire for providing the bonuses but argued they need to do something to attract the talent necessary to oversee $5 trillion in mortgage assets.
Earlier this month, the Federal Housing Finance Agency announced that the head of Fannie received $5.6 million in compensation and the chief executive of Freddie received $5.4 million.
Under the bill, the top executives of Fannie and Freddie could only have earned $218,978 this year.
Last week, Fannie’s chief executive Michael Williams announced he would step down from his position once a successor is found. That comes only three months after Freddie’s CEO Charles Haldeman Jr. announced that he will leave his post this year.
The government is being tasked to find replacements, not only for the two mortgage giants which have cost taxpayers more than $150 billion since their government takeover in 2008, but there is talk that the Obama administration is looking to replace FHFA acting director Edward DeMarco, the overseer of the GSEs.
In a letter to President Obama earlier this week, more than two dozen House members said DeMarco simply hasn’t done enough to help struggling homeowners avoid foreclosure.
The lawmakers are pushing the president to name a permanent director “immediately.”
Also, in December, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) sued six former executives at Fannie and Freddie, alleging they misled the public and investors about the amount of risky mortgages in their portfolio.
In the claims, the SEC contends that as the housing bubble began to burst, the executives suggested to investors that the GSEs were not substantially exposed to sub-prime mortgages that were defaulting across the country.
Related articles
- Can anyone save Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac? (money.cnn.com)
- CEO who led Fannie Mae after government seizure to quit (usatoday.com)
- SEC Sues Former Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Executives For Fraud (huffingtonpost.com)
- Fannie Mae CEO steps down during troubled times (agbeat.com)
- Fannie Mae CEO Steps Down, Despite Having “Long Way to Go in Housing” (inquisitr.com)
- The Future of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (money.usnews.com)
- Fannie, Freddie CEOs Took Millions, Far More Than Gingrich (pjmedia.com)
- Lawmakers slam Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac CEOs over pay and bonuses (latimesblogs.latimes.com)
-
Oregon’s Shadow Inventory – The “New Normal”?, by Phil Querin, Q-Law.com
The sad reality is that negative equity, short sales, and foreclosures, will likely be around for quite a while. “Negative equity”, which is the excess by which total debt encumbering the home exceeds its present fair market value, is almost becoming a fact of life. We know from theRMLS™ Market Action report that average and median prices this summer have continued to fall over the same time last year. The main reason is due to the volume of “shadow inventory”. This term refers to the amorphous number of homes – some of which we can count, such as listings and pendings–and much of which we can only estimate, such as families on the cusp of default, but current for the moment. Add to this “shadow” number, homes already 60 – 90 days delinquent, those already in some stage of foreclosure, and those post-foreclosure properties held as bank REOs, but not yet on the market, and it starts to look like a pretty big number. By some estimates, it may take nearly four years to burn through all of the shadow inventory. Digging deeper into the unknowable, we cannot forget the mobility factor, i.e. people needing or wanting to sell due to potential job relocation, changes in lifestyle, family size or retirement – many of these people, with and without equity, are still on the sidelines and difficult to estimate.
As long as we have shadow inventory, prices will remain depressed.[1] Why? Because many of the homes coming onto the market will be ones that have either been short sold due to negative equity, or those that have been recently foreclosed. In both cases, when these homes close they become a new “comp”, i.e. the reference point for pricing the next home that goes up for sale. [A good example of this was the first batch of South Waterfront condos that went to auction in 2009. The day after the auction, those sale prices became the new comps, not only for the unsold units in the building holding the auction, but also for many of the neighboring buildings. – PCQ]
All of these factors combine to destroy market equilibrium. That is, short sellers’ motivation is distorted. Homeowners with negative equity have little or no bargaining power. Pricing is driven by the “need” to sell, coupled with the lender’s decision to “bite the bullet” and let it sell. Similarly, for REO property, pricing is motivated by the banks’ need to deplete inventory to make room for more foreclosures. A primary factor limiting sales of bank REO property is the desire not to flood the market and further depress pricing. Only when market equilibrium is restored, i.e. a balance is achieved where both sellers and buyers have roughly comparable bargaining power, will we see prices start to rise. Today, that is not the case – even for sellers with equity in their homes. While equity sales are faster than short sales, pricing is dictated by buyers’ perception of value, and value is based upon the most recent short sale or REO sale.
So, the vicious circle persists. In today’s world of residential real estate, it is a fact of life. The silver lining, however, is that most Realtors® are becoming much more adept – and less intimidated – by the process. They understand these new market dynamics and are learning to deal with the nuances of short sales and REOs. This is a very good thing, since it does, indeed, appear as if this will be the “new normal” for quite a while.
Related articles
- Pre-Foreclosure Short Sales Jump 19% in Second Quarter by Carrie Bay, DSNEWS.com (oregonrealestateroundtable.com)
- Pre-Foreclosure Short Sales Jump 19% in Second Quarter (bingrealtygroup.wordpress.com)
- Home shadow inventory shrinks in July: CoreLogic (marketwatch.com)
- Housing crisis is not over (lansner.ocregister.com)
- Short Sale Mindset (velindapeyton.com)
- What is a Short Sale? And Other Commonly Asked Questions (mickeyknowsphilly.com)
- RealtyStore Reports First-Half 2010 Closes with More REO Foreclosure Inventory — REO Inventory Increases Expected through Q4 (prweb.com)
- Preferred Method of Home Liquidation by Banks – Short Sales Better Than Foreclosures (johnmurphyreports.com)
-
Court rulings complicate evictions for lenders in Oregon, by Brent Hunsberger, The Oregonian
Another Oregon woman successfully halted a post-foreclosure eviction after a judge in Hood River found the bank could not prove it held title to the home.
Sara Michelotti’s victory over Wells Fargo late last week carries no weight in other Oregon courts, attorneys say. But it illustrates a growing problem for banks — if the loans’s ownership history isn’t recorded properly, foreclosed homeowners might be able to fight even an eviction.
“There’s this real uncertainty from county to county about what that eviction process is going to look like for the lender,” said Brian Cox, a real estate attorney in Eugene who represented Wells Fargo.
Michelotti’s case revolved around a subprime mortgage lender, Option One Mortgage Corp., that went out of business during the housing crisis. Circuit Court Judge Paul Crowley ruled that it was not clear when or how Option One transferred Michelotti’s mortgage to American Home Mortgage Servicing Inc., which foreclosed on her home and later sold it to Wells Fargo.
Since the loan’s ownership was not properly recorded in Hood River County records, as required by Oregon law, Crowley ruled that Wells Fargo could not prove it had valid title to the property to evict. Crowley presides over courts in Hood River, Gilliam, Sherman, Wasco and Wheeler counties.
In June, a Columbia County judge blocked U.S. Bank’s eviction of Martha Flynn after finding the loan’s ownership history wasn’t properly recorded. But unlike Flynn’s case, Michelotti’s loan did not involve the Mortgage Electronic Registration Systems – a lightening rod for lawsuits over whether lenders properly foreclosed n homeowners.
“A lot of people get lost in ‘Oh it’s all MERS,’” said Michelotti’s attorney, Thomas Cutler of Harris Berne Christensen in Lake Oswego. “The problem runs broader than that.”
Crowley also rejected the bank’s argument that if Michelotti had paid her mortgage, the eviction would never have occurred.
“(Wells Fargo)’s counter argument to the effect that ‘if (Michelotti) had paid the mortgage we wouldn’t be here’ does not prevail at this junction because the question remains: are the right we here?’” Crowley wrote.
H&R Block Inc. sold Option One in 2008 to Wilbur Ross & Co., a distressed-asset investor, who merged it with American Home Mortgage Investment Corp.
But Crowley said he found no evidence of when the merger took place or why Option One’s name continued to be used on loan documents.
Cox said Wells Fargo had not yet decided how to respond to the ruling.
Related articles
- Court Rules Wells Fargo Cannot Sue Lac du Flambeau (indiancountrytodaymedianetwork.com)
- Thousands show up for Wells Fargo mortgage workshop (ajc.com)
- Homeowner’s Lawsuit Against Major Banks Progresses Slowly, Alleges Predatory Lending and Unfair and Deceptive Trade Practices by Wells Fargo and Others (prweb.com)
- New Program Helps Wachovia, Wells Fargo and World Savings Borrowers Get Relief from their Over-Mortgaged Homes (prweb.com)
- Wells Fargo Weighs Bid for a Belgian Private Bank (online.wsj.com)
-
Promoting Housing Recovery Part 3: Proposed Solutions For The Housing Market
This is the final part of a three-part, two-post series. Click here to read parts I and II, which focus on recognizing the fundamental economic problems, and fixing the underlying economic issues (such as unemployment)
Part Three – Proposed Solutions For The Housing Market
Home Prices
Home prices in many parts of the country are still inflated. People cannot afford the homes and cannot refinance to lower payments, so the homes go into default and are foreclosed up. Other homes remain on the market, vacant because there are no qualified buyers for the property at that price. This is a problem that can take care of itself over time, if the government gets out of the way.
Currently the government, in cooperation with banks, is doing everything to support home prices instead of letting them drop. Doing so prevents homeowner strategic defaults, and others going into defaults. It also lessens the losses to lenders and investors. In the words of Zig Zigler, this is “stinkin thinkin”.
Maintaining home prices artificially high will not stabilize the market. It is mistakenly thought this is the same as supporting home values. But inflating a price does not increase value, by definition. It just delivers an advantage to the first ones in at the expense of those coming later (think of the first and second homebuyer tax credits, which created two discernible “bumps” in home prices and sales in 2009 and 2010, both of which reversed).
We must allow home prices to drop to a more reasonable level that people can afford. Doing so will stimulate the market because it brings more people into the market. Lower home prices mean more have an ability to purchase. More purchases mean more price stability over a period of time.
To accomplish a reduction in home prices several steps need to be taken.
The first thing to be done is that the fed must cease its negative interest rate policy. Let interest rates rise to a level that the market supports. Quit subsidizing homeowner payments on adjustable rate mortgages by the lower interest rates.
Allowing interest rates to return to market levels would initially make homeownership more difficult and would result in people qualifying for lower loan amounts. However, this is not a bad thing because it eventually forces home prices down and all will balance out in the end. Historically, as interest rates decrease, home prices increase, and when rates increase, home prices drop. So it is time to let the market dictate where interest rates should be.
Furthermore, by allowing interest rates to increase, it makes lending money more attractive. Profit over risk levels return, and lenders are more willing to lend. This creates greater demand, and would assist in stabilizing the market.
We have to eliminate the Federal guarantee on Fannie and Freddie loans. The guarantee of F&F loans only serves to artificially depress interest rates. It does nothing to promote housing stability. Elimination of the guarantees would force rates up, leading to lower home values, and more affordability in the long run.
It is seriously worth considering privatizing Fannie and Freddie. Make them exist on their own without government intervention. Make them concerned about risk levels and liquidity requirements. Doing so will make them responsive to the profit motive, tighten lending standards, and lessen risk. It will over time also ensure no more government bailouts.
Allow competition for Fannie and Freddie. Currently, they have no competition and have not had competition since the early 1990s. Competition will force discipline on F&F, and will ultimately prove more productive for housing.
The new Qualified Residential Mortgage rules must not be allowed to occur as they stand. If the rules are allowed to go forward, it will only ensure that Fannie and Freddie remain the dominant force in housing. Make mortgage lending a level playing field for all. Do not favor F&F with advantages that others would not have like governmental guarantees. We must create effective competition to counter the distorting effects of F&F.
Government Programs like HAMP
When government attempts to slow or stop foreclosures, it only offers the homeowner false hopes that the home can be saved. The actions will extend the time that a homeowner remains in a home not making payments, and also extend the length of time that the housing crisis will be with us. Nothing else will generally be accomplished, except for further losses incurred by the lender or investor.
When modifications are advanced to people who have no ability to repay those modifications, when the interest rates adjust in five years, all that has happened is that the problem has been pushed off into the future, to be dealt with later. This is what government programs like HAMP achieve.
If the government wants to play a role in solving the housing crisis, it must take a role that will be realistic, and will lead to restoration of a viable housing market. That role must be in a support role, creating an economic environment which leads to housing recovery. It must not be an activist and interventionist role that only seeks to control outcomes that are not realistic.
Portfolio Lenders
Usually, the portfolio lender is a bank or other similar institution that is subject to government regulations, including liquidity requirements. Because of liquidity issues and capital, it is not possible for many banks to lend, or in sufficient numbers to have a meaningful effect upon housing recovery at this time. Additionally, the number of non-performing loans that lenders hold restricts having the funds to lend do to loan loss reserve issues. Until such is addressed, portfolio lending is severely restricted.
To solve the problem of non-performing loans, and to raise capital to address liquidity requirements, a “good bank – bad bank scenario” scenario must be undertaken. Individual mortgage loans need to be evaluated to determine the default risk of any one loan. Depending upon the risk level, the loan will be identified and placed into a separate category. Once all loans have been evaluated, a true value can be established for selling the loans to a “purchase investor”. At the same time, the “bank investor” is included to determine what capital infusion will be needed to support the lender when the loans are sold. An agreement is reached whereby the loans are sold and the new capital is brought into the lender, to keep the lender afloat and also strengthen the remaining loan portfolio.
The homeowner will receive significant benefit with this program. The “purchase investor” should have bought the loans for between 25 and 40 cents on the dollar. They can then negotiate with the homeowner, offering them significant principal reductions and lowered payments, while still having loans with positive equity. Default risk will have been greatly reduced, and all parties will have experienced a “win-win” scenario.
However, portfolio lending is still dependent upon having qualified borrowers. To that end, previous outlined steps must be taken to create a legitimate pool of worthy borrowers to reestablish lending.
Anyone who has followed the foreclosure crisis, the name MERS is well known. MERS (Mortgage Electronic Registrations System) represents the name of a computerized system used to track mortgage loans after origination and initial recording. MERS has been the subject of untold articles and conspiracy theories and blamed for the foreclosure process. It is believed by many that the operation of MERS is completely unlawful.
To restart securitization efforts, a MERS-like entity is going to be required. (MERS has been irrevocably damaged and will have to be replaced by a similar system with full transparency. Before anyone gets upset, I will explain why such an entity is required.)
Securitization of loans is a time consuming process, especially related to the tracking and recording of loans. When a loan is securitized, from the Cut-Off date of the trust to the Closing Date of the trust when loans must be placed into the trust, is 30 days. During this 30 day period of time, a loan would need to be assigned and recorded at least twice and usually three times. To accomplish this, each loan would need assignments executed, checks cut to the recorder’s office, and the documents delivered to the recorder’s office for recording.
Most recorder’s offices are not automated for electronic filing with less than 25% of the over 3200 counties doing electronic filing. The other offices must be done manually. This poses an issue in that a trust can have from several hundred to over 8000 loans placed into it. It is physically impossible to execute the work necessary in the 30 day time period to allow for securitization as MERS detractors would desire. So, an alternative methodology must be found.
“MERS 2.0″ is the solution. The new MERS must be developed with full transparency. It must be designed to absolutely conform with agency laws in all 50 states. MERS “Certifying Officers” must be named through corporate resolutions, with all supporting documentation available for review. There can be no question of a Certifying Officer’s authority to act.
Clear lines of authority must be established. The duties of MERS must be well spelled out and in accordance with local, state, and Federal statutes. Recording issues must be addressed and formalized procedures developed. Through these and other measures, MERS 2.0 can be an effective methodology for resolving the recording issues related to securitization products. This would alleviate many of the concerns and legal issues for securitization of loans, bringing greater confidence back into the system.
Securitization & Investors
Securitization of loans through sources other than Fannie and Freddie represented 25% of all mortgage loans done through the Housing Boom. This source of funding no longer exists, even though government bonds are at interest rates below 1%, and at times, some bonds pay negative interest. One would think that this would motivate Wall Street to begin securitization efforts again. However, that is not the case.
At this time, there is a complete lack of confidence in securitized loan products. The reasons are complex, but boil down to one simple fact: there is no ability to determine the quality of any one or all loans combined in a securitization offering, nor are the ratings given to the tranches of reliable quality for the same reasons. Until this can be overcome, there can be no hope of restarting securitization of loans. However, hope is on the way.
Many different companies are involved in bringing to market products and techniques that will address loan level issues. Some products involve verification of appraisals, others involve income and employment verification. More products are being developed as well. (LFI Analytics has its own specific product to address issues of individual loan quality.)
What needs to be done is for those companies developing the products to come together and to develop a comprehensive plan to address all concerns of investors for securitized products. What I propose is that we work together to incorporate our products into a “Master Product”, while retaining our individuality. This “Master Product” would be incorporated into each Securitization offered, so that Rating Agencies could accurately evaluate each loan and each tranche for quality. Then, the “Master Product” would be presented to Investors along with the Ratings Agency evaluation for their inspection and determination of whether to buy the securitized product. Doing so would bring confidence back into the market for securitized products.
There will also need to be a complete review of the types of loans that are to be securitized, and the requirements for each offering. Disclosures of the loan products must be clear, with loan level characteristics identified for disclosure. The Agreements need to be reworked to address issues related to litigation, loan modifications, and default issues. Access to loan documentation for potential lender repurchase demands must be clarified and procedures established for any purchase demand to occur.
There must be clarification of the securitization procedures. A securitized product must meet all requirements under state and Federal law, and IRS considerations. There must be clear guidance provided on how to meet the requirements, and what is acceptable, and what is not acceptable. Such guidance should seek to eliminate any questions about the lawfulness of securitization.
Finally, servicing procedures for securitization must be reviewed, clarified, and strengthened. There can no longer be any question as to the authority of the servicer to act, so clear lines of authority must be established and agency and power of attorney considerations be clearly written into the agreements.
Borrower Quality
Time and again, I have referenced having quality borrowers who have the ability to buy homes and qualify for loans. I have outlined steps that can be taken to establish such pools of buyers and borrowers by resolving debt issues, credit issues, and home overvaluation issues. But that is not enough.
Having examined thousands of loan documents, LFI Analytics has discovered that not only current underwriting processes are deficient in many areas still, but the new proposed Qualified Written Mortgage processes suffer from such deficiencies as well. This can lead to people being approved for loans who will have a high risk of default. Others will be declined for loans because they don’t meet the underwriting guidelines, but in reality they have a significantly lower risk of default.
Default Risk analysis must be a part of the solution for borrower quality. Individual default risk must be determined on each loan, in addition to normal underwriting processes, so as to deny those that represent high default risk, and approve those that have low default risk.
This is a category of borrower that portfolio lenders and securitization entities will have an advantage over the traditional F&F loan. Identifying and targeting such borrowers will provide a successful business model, as long as the true default risk is determined. That is where the LFI Analytics programs are oriented.
Summary
In this series of articles, I have attempted to identify stresses existing now and those existing in the future, and how the stresses will affect any housing recovery. I have also attempted to identify possible solutions for many of the stresses.
The recovery of the housing market will not be accomplished in the near future, as so many media and other types represent. The issues are far too complex and interdependent on each other for quick and easy remedy.
To accurately view what is needed for the housing recovery, one must take a macro view of not just housing, but also the economic and demographic concerns, as I have done here. Short and long term strategies must be developed for foreclosure relief, based upon the limiting conditions of lenders, borrowers, and investor agreements.
Lending recovery must be based upon the economic realities of the lenders, and the investors who buy the loans. Furthermore, accurate methods of loan evaluation and securitization ratings must be incorporated into any strategy so as to bring back investor confidence.
Are steps being taken towards resolving the housing crisis and beginning the housing recovery? In the government sector, the answer is really “no”. Short term “solutions” are offered in the form of different programs, but the programs are ineffective for most people. Even then, the “solutions” only treat the symptom, and not the illness. Government is simply not capable of taking the actions necessary to resolve the crisis, either from incompetence or from fear of voter reprisal.
In the private sector, baby steps are being taken by individual companies to resolve various issues. These companies are refining their products to meet the needs of all parties, and slowly bringing them to market.
What is needed now is for the private sector to come together and begin to offer “packages of products” to meet the needs of securitizing entities. The “packages” should be tailored to solve all the issues, so that all evaluation materials are complete and concise, and not just a handful of different reports from different vendors. This is the “far-sighted” view of what needs to be done.
If all parties cannot come together and present a unified and legitimate approach to solving the housing crisis, then we will see a “lost decade” (or two) like Japan has suffered. Housing is just far too important of an economic factor for the US economy. Housing has led the way to recovery in past recessions, but it not only lags now, it drags the economy down. Until housing can recover, it shall serve to be a drag on the economy.
I hope that I have sparked interest in what has been written and shall lead to a spirited discussion on how to recover. I do ask that any discussion focus on how to restore housing. Recriminations and blame for what has happened in the past serves no purpose to resolution of the problems facing us now, and in the future.
It is now time to move past the anger and the desire for revenge, and to move forward with “can-do” solutions.
Related articles
- Housing refinance proposal unfair to most homeowners (thehill.com)
- Government Officials Weigh New Refi Program, Carrie Bay, DSNEWS.com (oregonrealestateroundtable.com)
- Big changes on mortgages as ‘jumbo’ limits drop (sfgate.com)
- Who are Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac? (seattletimes.nwsource.com)
- Administration considering new mass refinancing scheme (dailykos.com)
- Republican on need for government role in housing (marketwatch.com)
- KHC Mortgage Interest Rates as of 08/28/2011 (kentuckyfirsttimehomebuyer.com)
- A New Threat to the Hottest Dividend Sector in the Market (fool.com)
- How Do I Know If My Mortgage Loan Is Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac? (thinkup.waldenu.edu)
- U.S. May Back Refinance Plan for Mortgages (georgegmiller.wordpress.com)
- Refinance a big mortgage before it’s too late… (sfgate.com)
- Inflation as a solution (geneveith.com)
- Fannie and Freddie will put foreclosed housing into rental market (dailykos.com)
-
Promoting Housing Recovery Parts 1 and 2, by Patrick Pulatie
Previously, I have posted articles regarding housing and foreclosure issues. The purpose was to begin a dialogue on the steps to be taken to alleviate the foreclosure crisis, and to promote housing recovery. Now, we need to explore how to restart lending in the private sector. This will be a three part article, with parts I and II herein, and III in the next post.
To begin, we must understand how we got to the point of where we are today, and whereby housing became so critical a factor in the economy. (This is only an overview. I leave it to the historians to fill in all the details.)
Part One – Agreeing On The Problems
Historical Backdrop
At the beginning of the 20th century, the U.S. population stood about 76,000,000 people. By the end of 2000, the population was over 310 million. The unprecedented growth in population resulted in the housing industry and related services becoming one of several major engines of wealth creation during the 20th century.
During the Depression, large numbers of farm and home foreclosures were occurring. The government began to get involved in housing to stop foreclosures and stimulate housing growth. This resulted in the creation of an FHA/Fannie Mae– like program, to support housing.
WWII led to major structural changes in the U.S., both economically and culturally. Manufacturing and technological changes spurred economic growth. Women entered the work force in huge numbers. Returning veterans came back from the war desiring to leave the rural areas, begin families, and enter the civilian workforce. The result was the baby boom generation and its coming influence.
From the 1950s through the 1970s, the US dominated the world economically. Real income growth was occurring for all households. Homeownership was obtainable for ever increasing numbers of people. Consumerism was rampant.
To support homeownership, the government created Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac so that more people could partake in the American Dream. These entities would eventually become the primary source of mortgages in the U.S. F&F changed the way mortgages were funded, and changed the terms of mortgages, so that 30 year mortgages became the common type of loan, instead of 5 to 15 year mortgages.
Storm clouds were beginning to appear on the horizon at the same time. Japan, Korea, Germany, and other countries had now come out of their post war depressions. Manufacturing and industrial bases had been rebuilt. These countries now posed an economic threat to the U.S. by offering improved products, cheaper labor costs, and innovation. By the end of the 1970s, for many reasons, US manufacturing was decreasing, and service related industries were gaining importance.
In the 1980s and 1990s, manufacturing began to decline in the U.S. Service Industries were now becoming a major force in the economy. With the end of the Cold War in 1989, defense spending began to decline dramatically, further depressing the economy.
In the early 1990s, F&F engaged in efforts to increase their share of the mortgage market. They freely admitted wanting to control the housing market, and took steps to do so, undermining lenders and competition, and any attempts to regulate them.
In 1994, homeownership rates were at 64% in the US. President Clinton, along with Congress and in conjunction with Fannie and Freddie, came out with a new program with the intent to promote a 70% homeownership rate. This program was promoted even though economists generally considered 64% to be the maximum amount of homeownership that an economy could readily support. Above 64%, people would be
“buying” homes, but without having the financial capabilities to repay a loan. The program focused upon low income persons and minorities. The result was greater demand for housing and homeownership, and housing values began to increase.
Lenders and Wall Street were being pushed out of the housing market by F&F, and had to find new markets to serve. F&F did not want to service the new markets being created by the government homeownership programs. The result was that Wall Street would naturally gravitate to that market, which was generally subprime, and also to the jumbo market, which F&F could not serve due to loan amount restrictions. This was the true beginning of securitized loan products.
The events of 9/11 would ultimately stoke the fires of home ownership even further. 9/11 occurred as the US was coming out of a significant recession, and to keep the country from sliding back into recession, the Fed lowered interest rates and kept them artificially low until 2003. Wall Street, recognizing the promise of good financial returns from securitized loans, freed up more and more capital for banks and mortgage bankers to lend. This led to even greater demand for homes and mortgages.
To meet the increased demand, home construction exploded. Ancillary services did well also, from infrastructure, schools, hospitals, roads, building materials, and home decor. The economy was booming, even though this was “mal-investment” of resources. (Currently, as a result of this activity, there are estimated to be from 2m to 3.5m in excess housing units, with approximately 400k being added yearly to housing stock.)
It did not stop there. Buyers, in their increasing zeal, were bidding for homes, increasing the price of homes in many states by 50 to 100,000 dollars more than what was reasonable. The perception was that if they did not buy now, then they could never buy. Additionally, investors began to purchase multiple properties, hoping to create a home rental empire. This led to unsustainable home values.
Concurrently, the Fed was still engaged in a loose money policy. This pumped hundreds of billions of dollars into the housing economy, with predictable results. With increasing home values, homeowners could refinance their homes, often multiple times over, pulling cash out and keeping the economy pumped up artificially. A homeowner could pull out 50,000 to 100,000 dollars or more, often every year or two, and use that money to indulge themselves, pretending they had a higher standard of living than what existed. The government knew that this was not a reasonable practice, but indulged in it anyway, so as to keep up an appearance of a healthy economy. Of course, this only compounded the problem.
The end result of the past 40 years of government intervention (and popular support for that intervention) has been a housing market that is currently overbuilt and still overvalued. In the meantime, real wages have not increased since the mid 1990s and for large numbers of the population, negative income growth has been experienced. Today, all segments of the population, homeowners especially so, are saddled with significant mortgage debt, consumer debt, and revolving credit debt. This has led to an inability on the part of the population to buy homes or other products. Until wage and debt issues are resolved, employment increases, and housing prices have returned to more reasonable values, there can be no housing recovery.
Current Status
As all know, the current status of housing in the US is like a ship dead in the water, with no ability to steer except to roll with the waves. A recap:
Private securitization once accounted for over 25% of all mortgage loans. These efforts are currently nonexistent except for one entity, Redwood Trust, which has issued one securitized offerings in 2010 and one in 2011. Other than this, Wall Street is afraid to invest in Mortgage Products (to say nothing of downstream investors).
Banks are unable to lend their own money, which represented up to 15% of all lending. Most banks are capital impaired and have liquidity issues, as well as unknown liabilities from bad loans dating to the bubble.
Additionally, banks are suffering from a lack of qualified borrowers. Either there is no equity in the home to lend on, or the borrowers don’t have the financial ability to afford the loan. Therefore, the only lending that a bank can engage in is to execute loans and sell them to Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, or VA and FHA. There are simply no other options available.
F&F are buying loans from the banks, but their lending standards have increased, so the loan purchases are down. F&F still distort the market because of government guarantees on their loans (now explicit instead of implicit), and they are still able to purchase loans above $700k, which was implemented in response to the housing crisis.
F&F are still having financial issues, with the government having bailed them out to the tune of $140b, with much more to come.
VA is buying loans and doing reasonably well, but they serve a tiny portion of the market.
FHA has turned into the new subprime, accepting credit challenged borrowers, and with loan to values of 95% or greater. Default rates on FHA loans are rising significantly, and will pose issues for the government when losses absorb all FHA loss reserves, which may have already happened (depending on how you look at the accounting).
The Mortgage Insurance companies are financially depressed, with PMI being forced to stop writing new policies due to loan loss reserves being depleted. Likely, they will cease business or be absorbed by another company. Other companies are believed to be similarly in trouble, though none have failed yet.
The US population is still overburdened with debt. It is believed that the household consumer debt burden is over 11%, for disposable income. This is far too high for effective purchasing of any products, especially high end. (There has been a lessening of this debt from its high of 14% in 2008, but this has primarily been the result of defaults, so most of those persons are not in a position to buy.)
Patrick Pulatie is the CEO of LFI Analytics. He can be reached at 925-522-0371, or 925-238-1221 for further information. http://www.LFI-Analytics.com, patrick@lfi-analytics.com.
Related articles
- Buffett says – “Blow Up a Lot of Houses!” (belpointe.com)
- Who are Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac? (seattletimes.nwsource.com)
- Government Officials Weigh New Refi Program, Carrie Bay, DSNEWS.com (oregonrealestateroundtable.com)
- Janis Bowdler: Latino Losses Jeopardize America’s Economic Future (huffingtonpost.com)
- Land Banks (axsmithlaw.wordpress.com)
- Fannie Mae promises to keep families in homes, but instead pressures banks to foreclose (seattletimes.nwsource.com)
- Housing refinance proposal unfair to most homeowners (thehill.com)
- Fannie Mae Conservator Sued by Pension Funds Over Recovery Limit (businessweek.com)
- NYT: US may back refinance plan for mortgages (msnbc.msn.com)